Kria KV260 Example
Introduction
We will now paste the code of the example application of the SmartLock running on a Kria SOM (in our case a KV260 board) and explain how it works piece by piece.
The project is composed of 4 main classes:
easy_zmq, which implements the communication between the software and MuseBox Server using ZMQ library;easy_ncurses, which is used to manage the information showed in the console window;cv_show, which exposes some functions to draw a graphic interface;camera2d, which handles 2D camera functions;
We use ncurses library to have a better output displayed in the terminal window.
Then, we now dig step by step and explain all the software functionalities.
Click to expand the entire main.cpp content
// #include <royale.hpp>
#include "../include/utils.hpp"
#include "../include/camera2d.hpp"
#include "../include/cv_show.hpp"
#include "../include/3d_face_points.hpp"
#include "../include/easy_zmq.hpp"
#include "../include/easy_ncurses.hpp"
#include "../include/point_cloud/feature_extractor_3d.hpp"
#include "../include/point_cloud/downsampler.hpp"
#include "../include/point_cloud/segmenter.hpp"
#include "../include/libroyale3d/LibRoyale3D.hpp"
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_person(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_clustered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 3)
{
std::cerr << " need as input the number of the camera and similarity" << std::endl;
}
unsigned int index = std::atoi(argv[1]);
float similarity_ = std::atof(argv[2]);
int listening_port = 5556;
bool unlocked = false;
int button_pressed = -1;
bool debug = false;
bool show = false;
bool ncur_active = true;
bool fullscreen = true;
for (int j = 3; j < argc; ++j)
{
if (strcmp(argv[j], "--debug") == 0)
{
debug = true;
std::cout << "Debug mode activated." << std::endl;
}
if (strcmp(argv[j], "--show") == 0)
{
show = true;
std::cout << "Show mode activated." << std::endl;
}
if (strcmp(argv[j], "--port") == 0)
{
listening_port = std::atoi(argv[++j]);
std::cout << "Subscriber will listen to port " << listening_port << "." << std::endl;
}
if (strcmp(argv[j], "--no-ncur") == 0)
{
ncur_active = false;
std::cout << "Removed ncurses" << std::endl;
}
if (strcmp(argv[j], "--no-fullscreen") == 0)
{
fullscreen = false;
std::cout << "Removed fullscreen mode" << std::endl;
}
}
std::string version = PROJECT_VER;
/*************************************** ZMQ ***************************************/
std::string listening_url = "tcp://127.0.0.1:" + std::to_string(listening_port);
std::string publishing_url = "tcp://127.0.0.1:9696";
easy_zmq zmq(27000);
void *publisher = zmq.create_publisher();
void *subscriber = zmq.create_subscriber();
zmq.bind_publisher(publisher, publishing_url);
zmq.connect_subscriber(subscriber, listening_url, "");
zmq.handshake(publisher);
/*************************************** 3D part with new library ***************************************/
LibRoyale3D libroyale = LibRoyale3D();
std::cout << LOG_3D_CAMERA("Camera connected") << std::endl;
segmenter *ec = new segmenter();
feature_extractor_3d *fe = new feature_extractor_3d(metrics::L2);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < face_points.size(); ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = face_points.at(i).at(0);
point.y = face_points.at(i).at(1);
point.z = face_points.at(i).at(2);
cloud_person->push_back(point);
}
/*************************************** 2D part ***************************************/
camera2d camera2d(index);
camera2d.open();
bool camera2d_detected = camera2d.detected();
/*************************************** Init ***************************************/
easy_ncurses ncur(version, debug, ncur_active);
ncur.write_init();
std::map<std::string, int> bounding_box;
cv_show cv_show("SmartLock Routine - v" + version, fullscreen);
cv::Mat image;
int mb_status;
int OK_THRESHOLD = 3;
int ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
std::string previousPerson = "";
while (camera2d_detected && libroyale.DETECTED) {
try{
if(show && !cv_show.draw_image(image, mb_status)){
break;
}
ncur.set_face_detection(FACE_DETECTED == 1);
ncur.set_face_recognition(FACE_DETECTED == 1, FACE_RECOGNIZED);
if(unlocked){
button_pressed = -1;
while(button_pressed != 114){
button_pressed = cv::waitKey(1);
if(button_pressed == 27){
zmq.close_connection(publisher);
zmq.close_connection(subscriber);
return 0;
}
continue;
}
unlocked = false;
}
camera2d_detected = camera2d.detected();
ncur.set_cameras_status(camera2d_detected, libroyale.DETECTED);
image = camera2d.capture();
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 0);
ncur.clear_lines(19, 1);
ncur.clear_lines(14, 1);
if (!libroyale.LOCKED) {
libroyale.lock();
*cloud = libroyale.get_camera_point_cloud();
if (libroyale.has_captured() && cloud->points.size() > 1) {
*cloud_clustered = ec->clustering(cloud);
std::tuple<float, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>> features = fe->get_features(cloud_clustered, cloud_person);
float similarity = std::get<0>(features);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::iterator begin_pcl = cloud->begin();
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::iterator end_pcl = cloud->end();
cloud->erase(begin_pcl, end_pcl);
if(debug){
ncur.write_similarity(similarity_, similarity);
}
if(similarity >= similarity_){
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
libroyale.unlock();
continue;
}
} else {
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
libroyale.unlock();
continue;
}
libroyale.unlock();
} else {
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
libroyale.unlock();
continue;
}
FACE_DETECTED = 1;
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 0);
// face detection task
nlohmann::json fd_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_DETECTION], publishing_url, listening_url, image);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fd_message.dump());
nlohmann::json fd_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
// check if there is only 1 face
if (json_key_exists(fd_response, "data")){
if(show) {
cv_show.draw_bounding_boxes(image, fd_response["data"]);
}
if(fd_response["data"].size() == 0){
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
} else if (fd_response["data"].size() == 1) {
ncur.clear_lines(19, 1);
int x = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["x"].get<int>();
int y = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["y"].get<int>();
int width = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["width"].get<int>();
int height = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["height"].get<int>();
bounding_box = cv_show.set_bounding_box(x, y, width, height);
std::string personFound = "";
std::vector<float> landmarks = {0};
cv::Mat cropped_face;
if(bounding_box["width"] < cv_show::BB_LIMIT){
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 2);
} else {
// face recognition
cropped_face = crop_face(image, bounding_box);
if (!cropped_face.empty()) {
nlohmann::json fr_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_RECOGNITION], publishing_url, listening_url, cropped_face);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fr_message.dump());
nlohmann::json fr_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
personFound = fr_response["data"]["prediction"] == "unknown" ? "" : fr_response["data"]["prediction"];
if(strcmp(personFound.c_str(), "") == 0){
// face not recognized
// face landmark
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 2);
nlohmann::json fl_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_LANDMARK], publishing_url, listening_url, cropped_face);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fl_message.dump());
nlohmann::json fl_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
landmarks = fl_response["data"]["prediction"].get<std::vector<float>>();
std::string ld_log(cv_show.draw_landmarks(image, bounding_box, landmarks, debug));
int ld_line = 14;
ncur.clear_lines(ld_line, 4);
ncur.write_line(ld_log, ld_line);
} else {
// face recognized
if(std::strcmp(previousPerson.c_str(), personFound.c_str()) == 0){
if(ok_count-- <= 0){
FACE_RECOGNIZED = personFound;
cv_show.draw_thumbnail(image, personFound);
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 1);
cv_show.draw_name(image, personFound, bounding_box);
cv_show.door_unlocked(image);
unlocked = true;
}
} else {
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
}
}
}
}
previousPerson = personFound;
} else {
// here there are more than 1 face
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
ncur.write_line("There must be only 1 face", 19);
}
}
} catch(std::exception &e){
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
libroyale.unlock();
ncur.write_init();
continue;
}
}
// destroy
zmq.close_connection(publisher);
zmq.close_connection(subscriber);
return 0;
}
Variables
Some of the most important variables used into the code are:
index: 2D camera index;similarity_: it sets the 3D threshold to accept something in front of the camera as a face;min_epsilon: it is the similarity threshold for the Face Recognition task;listening_port: it is the port where the software listens to the MuseBox Server responses;
ZMQ
First of all, we must set the communication between the software and the MuseBox Server using our easy_zmq class.
The zmq object receives as input the buffer length, which is set to 27000 by default.
std::string listening_url = "tcp://127.0.0.1:" + std::to_string(listening_port);
std::string publishing_url = "tcp://127.0.0.1:9696";
easy_zmq zmq(27000);
void *publisher = zmq.create_publisher();
void *subscriber = zmq.create_subscriber();
zmq.bind_publisher(publisher, publishing_url);
zmq.connect_subscriber(subscriber, listening_url, "");
zmq.handshake(publisher);
Publisher
The creation of the publisher is entrusted to the appropriate function:
void* easy_zmq::create_publisher(){
void* publisher = zmq_socket(context, ZMQ_PUB);
assert(publisher);
return publisher;
}
The connection to the listening url is created with the following function:
void easy_zmq::bind_publisher(void* publisher, std::string publishing_url){
int bind = zmq_bind(publisher, publishing_url.c_str());
if (bind < 0) {
unsigned int error_code = zmq_errno();
std::cout << "zmq_bind server ctx error: " << error_code << ", " << zmq_strerror(error_code) << "\n" << std::endl;
assert(bind == 0);
}
}
Subscriber
The creation of the subscriber is entrusted to the appropriate function:
void* easy_zmq::create_subscriber() {
void* subscriber = zmq_socket(context, ZMQ_SUB);
assert(subscriber);
return subscriber;
}
The subscriber connection is made by the following function:
void easy_zmq::connect_subscriber(void* subscriber, std::string listening_url, std::string topic){
int connect = zmq_connect(subscriber, listening_url.c_str());
if(connect < 0){
std::cout << "Subscriber not connected" << std::endl;
}
int rc = zmq_setsockopt(subscriber, ZMQ_SUBSCRIBE, reinterpret_cast<void*>(&topic), 0);
int timeout = 500;
zmq_setsockopt(subscriber, ZMQ_RCVTIMEO, &timeout, sizeof(timeout));
}
Handshake
The handshake phase is necessary to initialize the communication with MuseBox Server. It is made by:
void easy_zmq::handshake(void* publisher) {
nlohmann::json message = {{"topic", "Handshake"}};
int out = easy_zmq::send_message(publisher, message.dump());
sleep(1);
std::cout << "Handshake done..." << std::endl;
}
that it simply sends a message with the topic set to Handshake.
3D Camera
The following code refers to the 3D ToF camera. Please take a look also to 3D APIs section for more information about the 3D APIs used by these pieces of code.
We have used a custom library named LibRoyale3D to easily manage the APIs. In our main file the initialization of the 3D camera is made with the code below. In fact, to initialize and make all the needed checks about the 3D camera, we must easily initialize our library with the following call:
LibRoyale3D libroyale = LibRoyale3D();
std::cout << LOG_3D_CAMERA("Camera connected") << std::endl;
Once the libroyale variable is defined, we are aware about the 3D camera connection and initialization. Let's deeply analize the content of this library. Most of the functions return a status code which indicates the status of the connection.
LibRoyale3D library
In this chapter we are going to explain all the functions exposed by our LibRoyale3D library.
Constructor
First of all, the constructor of our library is able to make some checks and initializations, such as the 3D camera detection, its initialization, the setting of some filters, etc.:
LibRoyale3D::LibRoyale3D() {
status st = detect();
DETECTED = st == status::STATUS_OK;
if(!DETECTED){
return;
}
st = initialize();
INITD = st == status::STATUS_OK;
if(!INITD){
return;
}
retrieve_streams();
set_filters();
camera->registerDataListener(&depth_data_listener);
if(DETECTED && INITD){
start_capture();
}
LOCKED = depth_data_listener.guard;
INFO = std::string("LibRoyale3D - v") + std::string(LIBROYALE3D_PROJECT_VER) + std::string(" - MakarenaLabs SRL");
}
3D camera detection
The first action of the construction is the detection of the 3D camera. It is made by the following function:
status LibRoyale3D::detect(){
royale::CameraManager manager;
royale::Vector<royale::String> camera_list;
camera_list = manager.getConnectedCameraList();
if (camera_list.empty()) {
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "No 3D camera detected" << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_DETECTED;
}
camera = manager.createCamera(camera_list[0]); // we have only one camera connected!!!
if (camera == nullptr) {
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Can not create the 3D camera" << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_CREATED;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "3D camera detected" << std::endl;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
3D camera initialization
Then, we initialize the camera:
status LibRoyale3D::initialize(){
// Before the camera device is ready we have to invoke initialize on it.
if (camera->initialize() != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
{
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Cannot initialize the 3D camera" << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_INITIALIZED;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "3D camera initialized" << std::endl;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
Setting the 3D camera options
After the camera initialization, we set the density of the depth information in input:
status LibRoyale3D::retrieve_streams(){
if (camera->getStreams(streamIds) != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
{
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Cannot retrieve streams from the 3D camera" << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_STREAMS;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "Retrieving streams from the 3D camera" << std::endl;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
status LibRoyale3D::set_filters(){
#if LIBROYALE_VERSION == 4
if (camera->setFilterLevel(royale::FilterPreset::Binning_8_Basic, streamIds[0]) != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
#else
if (camera->setFilterPreset(royale::FilterPreset::Binning_8_Basic, streamIds[0]) != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
#endif
{
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Cannot set filter for stream " << std::to_string(streamIds[0]) << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_FILTERS;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "Set filter for stream " << std::to_string(streamIds[0]) << std::endl;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
Starting to capture of the data
If all the previous steps end without any problems, we start to obtain the 3D data. To do this, we attach a callback function which will convert the depth information in a Point Cloud and return it for our 3D processing branch:
status LibRoyale3D::start_capture(){
// start capture mode
if (camera->startCapture() != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
{
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Error starting the capturing" << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_CAPTURE;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "Ready to capture data" << std::endl;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
Setting the exposure time
Finally, we set the exposure time of the camera:
status LibRoyale3D::set_exposure_time(int exposure){
if (camera->setExposureTime(exposure, streamIds[0]) != royale::CameraStatus::SUCCESS)
{
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][ERROR] " << "Cannot set exposure time for stream " << std::to_string(streamIds[0]) << std::endl;
return status::NO_CAMERA_EXPOSURE_TIME;
}
std::cout << "[LIBROYALE3D][INFO] " << "Changed exposure time for stream " << std::to_string(streamIds[0]) << " to " << exposure << " microseconds" << std::endl;
exposure_time = exposure;
return status::STATUS_OK;
}
If all the previous tasks run correctly, we have successfully connected the 3D camera:
std::cout << LOG_3D_CAMERA("Camera connected") << std::endl;
2D camera
Now, we are ready to initialize the 2D camera using our class, passing as input its index:
camera2d camera2d(index);
camera2d.open();
bool camera2d_detected = camera2d.detected();
Initialization
Previously, we initialize the 2D camera object passing as input its index:
camera2d::camera2d(int _index) {
index = _index;
}
Camera aperture
Once we have opened the camera, we can start capturing the frames. This piece of code uses OpenCV to init the camera in the cap class global variable and checks whether it is connected or not.
Then, it assigns True to the DETECTED class global variable if the camera is ready and opened, False otherwise.
void camera2d::open(){
if(index < 0){
index = get_index(15);
}
cap.open(index);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cerr << LOG_2D_CAMERA("Cannot open camera") << std::endl;
DETECTED = false;
} else {
cap.set(cv::CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 1);
try {
cv::Mat test_image;
cap.read(test_image);
DETECTED = true;
std::cout << LOG_2D_CAMERA("Camera connected") << std::endl;
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << LOG_2D_CAMERA("Cannot open camera") << std::endl;
DETECTED = false;
}
}
}
Processing branches
The software processing flow is divided into two parts:
Face Detection, Face Recognition and Face Landmark AI tasks are included inside the 2D processing phase.
3D Processing
The first procedure which our SmartLock loop executes is the 3D processing branch. This branch receives the Point Cloud from the callback of the 3D camera.
The first operation is to segment the face out of the Point Cloud received with the segmenter object:
*cloud_clustered = ec->clustering(cloud);
The second operation is to extract the features and the similarity of what is in front of the camera to a 3D face
std::tuple<float, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>> features = fe->get_features(cloud_clustered, cloud_person);
float similarity = std::get<0>(features);
If the Point Clouds are similar, in front of the camera there is an actual face, and we can proceed, otherwise we restart the loop
if(similarity >= similarity_){
FACE_DETECTED = 0;
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
libroyale.unlock();
continue;
}
2D Processing and Recognition
The last step, if an actual 3D face is found in front of the camera, is to recognize it. This part of the code does the recognition task, which is composed by:
- Face Detection;
- Face Recognition;
- Face Landmark (to suggest the user to stay straight in front of the camera);
Before the 3D processing phase (we did this before to have a continuity in the display of images with OpenCV), we have captured the camera frame using the camera2d class:
image = camera2d.capture();
where the function is:
cv::Mat camera2d::capture(){
// grab 2D camera frame
cv::Mat local_image;
cap.read(local_image);
cv::resize(local_image, local_image, cv::Size(IMG_WIDTH, IMG_HEIGHT));
cv::putText(local_image, "Press 'Esc' to close SmartLock Routine", cv::Point(10, IMG_HEIGHT-10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.2, BLACK, 3);
cv::putText(local_image, "Press 'Esc' to close SmartLock Routine", cv::Point(10, IMG_HEIGHT-10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.2, WHITE, 1.5);
return local_image;
}
which returns our frame (resized to be compatible with the AI models) as cv::Mat object.
With this frame, we can proceed with the entire recognition flow, which is:
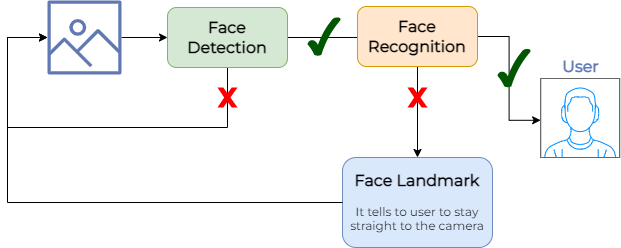
Fig. 1 - SmartLock Recognition Flow
MuseBox messages exchange
For all the following task, MuseBox needs the same message's structure.
nlohmann::json create_mb_message(std::string topic, std::string publishing_url, std::string listening_url, cv::Mat image, double min_epsilon)
{
// create the vector that "flats" the cv::Mat in a single dimension
std::vector<uchar> img_buf;
cv::imencode(".jpg", image, img_buf);
auto *enc_msg = reinterpret_cast<unsigned char *>(img_buf.data());
std::string encoded = base64_encode(enc_msg, img_buf.size());
nlohmann::json message = {
{"clientId", "1"}, // client ID
{"topic", topic}, // Machine Learning task
{"publisherMusebox", publishing_url},
{"publisherQueue", listening_url}, // where the MuseBox subscriber will respond
{"image", encoded}, // image to infer
};
if (topic != topic_name[topics::FACE_DETECTION])
{
message["only_face"] = true;
}
if (topic == topic_name[topics::FACE_RECOGNITION])
{
message["min_epsilon"] = min_epsilon; // face recognition threshold
}
return message;
}
In this function, first of all, we need to compress our image before sending it to the server. We do that with:
// create the vector that "flats" the cv::Mat in a single dimension
std::vector<uchar> img_buf;
cv::imencode(".jpg", image, img_buf);
auto *enc_msg = reinterpret_cast<unsigned char *>(img_buf.data());
std::string encoded = base64_encode(enc_msg, img_buf.size());
Then, we are able to prepare the JSON request to be sent:
nlohmann::json message = {
{"clientId", "1"}, // client ID
{"topic", topic}, // Machine Learning task
{"publisherMusebox", publishing_url},
{"publisherQueue", listening_url}, // where the MuseBox subscriber will respond
{"image", encoded}, // image to infer
};
For Face Recognition and Face Landmark tasks, we have to send the only_face flag set to True.
Only for Face Recognition task, we have to send the min_epsilon threshold.
if (topic != topic_name[topics::FACE_DETECTION])
{
message["only_face"] = true;
}
if (topic == topic_name[topics::FACE_RECOGNITION])
{
message["min_epsilon"] = min_epsilon; // face recognition threshold
}
Now we are ready to send and receive the messages to/from MuseBox Server. To do that, we use two functions:
int easy_zmq::send_message(void* publisher, std::string message){
int output = zmq_send(publisher, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0);
if (output < 0) {
unsigned int error_code = zmq_errno();
std::cout << "server ctx error: " << error_code << ", " << zmq_strerror(error_code) << "\n" << std::endl;
}
return output;
}
nlohmann::json easy_zmq::receive_message(void* subscriber){
// blocking receive for ZMQ
int nbytes = zmq_recv(subscriber, buffer, buffer_length, 0);
std::string str_msg = buffer;
if(str_msg == "" || str_msg.size() == 0 || nbytes == -1){
str_msg = "{}";
}
nlohmann::json message = nlohmann::json::parse(str_msg);
std::fill_n(buffer, buffer_length, 0);
return message;
}
Face Detection
The Face Detection phase starts with the creation of the message to send to the MuseBox Server:
// face detection task
nlohmann::json fd_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_DETECTION], publishing_url, listening_url, image, 0);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fd_message.dump());
ncur.clear_lines(19, 1);
nlohmann::json fd_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
once a face is detected (only 1 face is permitted):
if (fd_response["data"].size() == 1) {
ncur.clear_lines(19, 1);
int x = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["x"].get<int>();
int y = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["y"].get<int>();
int width = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["width"].get<int>();
int height = fd_response["data"][0]["boundingBox"]["height"].get<int>();
bounding_box = cv_show.set_bounding_box(x, y, width, height);
std::string personFound = "";
std::vector<float> landmarks = { 0 };
cv::Mat cropped_face;
[...]
}
we save the bounding box's dimensions received from MuseBox Server, and we can go ahead with the next phase.
Face Recognition
The next step is to send the image of the face detected to the MuseBox Face Recognition task. To do this, we must crop the image following the bounding box's dimensions:
cropped_face = crop_face(image, bounding_box);
where the crop_face function is:
cv::Mat crop_face(cv::Mat image, std::map<std::string, int> bounding_box)
{
cv::Mat cropped_face;
cv::Rect roi;
roi.x = bounding_box["x"];
roi.y = bounding_box["y"];
roi.width = bounding_box["width"];
roi.height = bounding_box["height"];
try
{
cropped_face = image(roi);
}
catch (cv::Exception &e)
{
std::cout << "Couldn't crop image." << std::endl;
}
return cropped_face;
}
Then, we can set and send the Face Recognition message to the MuseBox Server. If the person is recognized, its name is saved into personFound variable.
If the MuseBox Server returns unknown value, personFound variable is set to empty string.
nlohmann::json fr_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_RECOGNITION], publishing_url, listening_url, cropped_face, min_epsilon);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fr_message.dump());
nlohmann::json fr_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
personFound = fr_response["personFound"] == "unknown" ? "" : fr_response["personFound"];
Here two scenarios open up:
- Face is recognized;
- Face is not recognized;
The detected face is recognized when personFound variable is not empty. In this case, we want to be sure that the recognized person in this turn is the same of the last one.
A person is recognized when it is the same for 3 consecutive times (int OK_THRESHOLD = 3;).
// face recognized
if(std::strcmp(previousPerson.c_str(), personFound.c_str()) == 0){
if(ok_count-- <= 0){
FACE_RECOGNIZED = personFound;
cv_show.draw_thumbnail(image, personFound);
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 1);
cv_show.draw_name(image, personFound, bounding_box);
}
} else {
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
}
Otherwise, if the person is not recognized, it could be they are not facing straight to the camera. To suggest them to do so, we use Face Landmark task.
Face Landmark
First of all, we must send the message to the MuseBox Server, and we must wait the response:
// face not recognized
// face landmark
FACE_RECOGNIZED = "0";
ok_count = OK_THRESHOLD;
cv_show.draw_circles(image, 2);
nlohmann::json fl_message = create_mb_message(topic_name[topics::FACE_LANDMARK], publishing_url, listening_url, cropped_face, 0);
mb_status = zmq.send_message(publisher, fl_message.dump());
nlohmann::json fl_response = zmq.receive_message(subscriber);
The MuseBox Server returns the array of landmark points we can use whether to suggest or not to the user to face straight in front of the camera.
landmarks = fl_response["landmarks"].get<std::vector<float>>();
std::string ld_log(cv_show.draw_landmarks(image, bounding_box, landmarks, debug));
In the draw_landmarks function, we use three landmark points:
- Nose
- Left ear
- Right ear
We check the pan and the roll of the person's face. If the distance between the three points is out of the threshold, we show the suggestion.
std::string cv_show::draw_landmarks(cv::Mat image, std::map<std::string, int> bounding_box, std::vector<float> landmarks, bool debug)
{
std::string to_return = "";
std::vector<int> points = {57, 0, 32};
int nose = 57;
int ear_sx = 0;
int ear_dx = 32;
// panning
float dx_nose_distance = std::sqrt(std::pow(landmarks[nose*2] - landmarks[ear_dx*2], 2) + std::pow(landmarks[nose*2+1] - landmarks[ear_dx*2+1], 2));
float sx_nose_distance = std::sqrt(std::pow(landmarks[nose*2] - landmarks[ear_sx*2], 2) + std::pow(landmarks[nose*2+1] - landmarks[ear_sx*2+1], 2));
float pan_threshold = 30;
// rolling
float ears_distance = std::abs(landmarks[ear_dx*2+1] - landmarks[ear_sx*2+1]);
float roll_threshold = 30;
if(std::abs(dx_nose_distance - sx_nose_distance) > pan_threshold || ears_distance > roll_threshold){
std::string _msg = "Please, keep your face straight";
cv::putText(image, _msg, cv::Point(bounding_box["x"]+10, bounding_box["y"]+bounding_box["height"]-10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, BLACK, 3);
cv::putText(image, _msg, cv::Point(bounding_box["x"]+10, bounding_box["y"]+bounding_box["height"]-10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, WHITE, 1.5);
to_return = "[WARN] - " + _msg;
}
[...]
}